Basic Concepts of Electrical Circuits
Power of Independent Sources
Determine the power of each source.
a)

b)

a)

b)

Solution
a) The current source keeps the current of the loop

For the voltage source the current enters from the positive terminal. Therefore, the passive sign convention should be used to find the sign of power:
For the current source, the current leaves from the positive terminal. Hence, the active sign convention should be used:
b) Similarily, the voltage across the current source and the currentpassing through thevoltage source can be easily determined by voltage and current sources, respectively:

For this problem, the current enters to the voltage source from the negative terminal. Thus, the active sign convention should be used:
Current of A Voltage Source
Find the current passing through the voltage source:
a)

b)

a)

b)

Solution
a) The voltage source is in series with the current source. Since by definition a current source keeps the current passing through itself constant and the voltage source is in series with the current source, it should have the same current


Voltage of A Current Source
Find voltages across the current sources.
a)

b)

c)

d)

e)

a)

b)

c)

d)

e)

Solution
In each case, the current source is parallel with a voltage source. Therefore, the voltage across the current source is equal to the voltage of the voltage source, regardless of other elements.
a)

b)

c)

d)

e)

Elements, Nodes, Loops and Branches
Solution
8 elements
6 nodes, as shown:
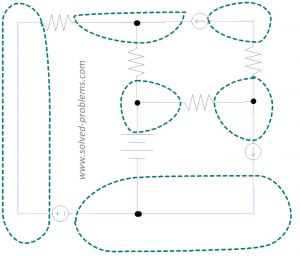
7 loops, as shown:
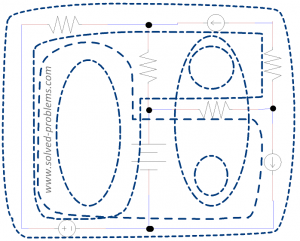
8 branches
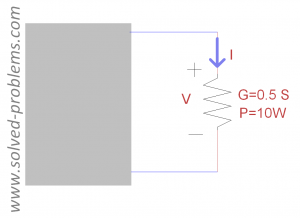
Using Power and Conductance
Solution
There are two answers:
a)
b)
Power and Conductance of Resistors
Determine the power absorbed by the resistors, the conductance of the resistors and  .
.
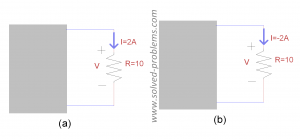
Solution
a)
b)
Power of Elements
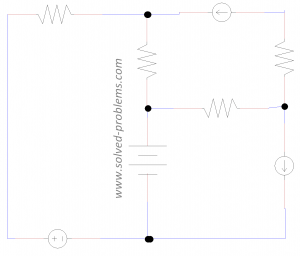
Find the power of each element. Which one is supplying power and which one is absorbing it?

Solution
a) Passive sign convention,
b) Passive sign convention,
d) Active sign convention,
Comments
Post a Comment